The ESRS (European Sustainability Reporting Standards) is emerging as a game changer as businesses navigate an increasingly complex landscape of sustainability requirements. But what exactly are these standards, and why are they critical to the future of corporate reporting? In this article, we’ll uncover how the ESRS can help future-proof your business and why understanding them is vital for long-term success.
1. Introduction to ESRS and its importance
What is ESRS?
The ESRS is a set of sustainability reporting standards developed under the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD). These standards were developed by the EFRAG, the European Financial Reporting Advisory Group, and aim to ensure that companies operating in Europe provide transparent, comparable, and reliable sustainability information. Adopted in July 2023 by the European Commission, they provide clear guidelines for businesses on what information to include in their sustainability reports and how to present it. Unlike the broad and often unclear NFRD guidelines (the predecessor of the CSRD), the ESRS introduces a more detailed and specific framework.
You can access the list of data points here.
Why is it critical for business reporting in 2024?
As regulatory pressures mount, and the CSRD states that all reporting must be in accordance with the ESRS, companies that fail to comply not only risk falling behind competitors and damaging their reputation, but might also face an indictment. It’s not just about meeting compliance—it’s about building trust with stakeholders and aligning your business with a more sustainable future. Adopting the ESRS enables organizations to stay ahead of evolving regulations and growing demands from investors, consumers, and regulators for transparent ESG data.
2. Understanding the core components of the ESRS
There are 12 ESRS Guidelines that specify the exact information that must be included in reports to provide a clear picture of the sustainability efforts of a company. The standards ensure that data is comparable across industries and different companies while guaranteeing that stakeholders can trust that the information is collected and presented according to a defined, consistent framework.
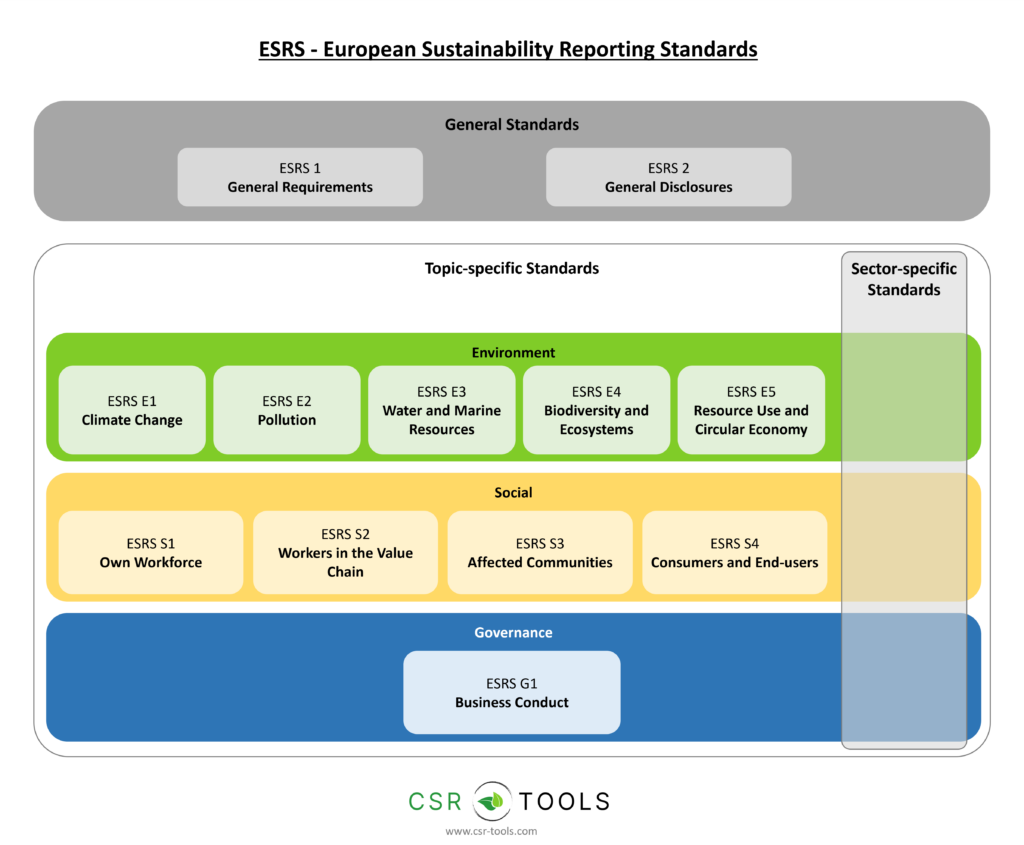
The ESRS are organized into three categories:
- General Standards: These include ESRS 1 (“General Requirements”), which establish the overarching principles for reporting under the ESRS framework, without mandating specific disclosure requirements, and ESRS 2 (“General Disclosures”), which outline key information that must be disclosed, regardless of the specific sustainability topic being addressed.
- Topic-specific Standards: Cover areas like climate change, biodiversity, and social matters, providing detailed guidelines beyond the general standards.
- Sector-specific Standards: Address industry-specific issues, enhancing comparability within sectors. These have been delayed until 2026 for industries like oil, gas, and automotive.
These are the 12 ESRS:
ESRS 1 – General Requirements
ESRS 2 – General Disclosures
E1 – Climate Change
E2 – Pollution
E3 – Water and Marine Resources
E4 – Biodiversity and Ecosystems
E5 – Resource Use and Circular Economy
S1 – Own Workforce
S2 – Workers in the Value Chain
S3 – Affected Communities
S4 – Consumers and End-users
G1 – Business Conduct
How the ESRS align with CSRD
The CSRD mandates that companies operating in the EU adhere to ESRS guidelines for their sustainability reporting. This alignment ensures that businesses across Europe follow consistent standards, making sustainability data comparable and actionable. This is an important step towards achieving the EU’s ambitious goal of making Europe the first climate-neutral continent by 2050 (as outlined in the European Green Deal) because it allows government authorities to measure progress towards the Green Deal objectives.
3. Future-proofing your business with ESRS
Adopting the ESRS is not just about meeting current requirements—it’s about future-proofing your business. Companies that embrace the standards can anticipate and respond more effectively to future sustainability trends, regulatory changes, and stakeholder expectations. It also helps address the challenge of managing climate change by identifying future risks to businesses and preventing them. For instance, assessing flood risk could lead to investments in flood-resistant technology and infrastructure, reducing the chances of future business disruptions. The data provided by the ESRS also assists governments in identifying obstacles and challenges faced by businesses, enabling them to take appropriate support measures—benefiting your company in the long term.
4. Double Materiality: The heart of ESRS compliance
At the core of the CSRD and ESRS is the concept of double materiality. This means that companies must report on:
- Financial materiality, or how sustainability factors affect the company’s financial position.
- Impact materiality, or how the company’s activities impact the environment and society.
Double materiality broadens the scope of traditional reporting by requiring companies to consider both internal and external impacts. This shift ensures that companies focus on issues that matter most to stakeholders, leading to more comprehensive and meaningful sustainability reports.
To implement double materiality, companies must conduct a materiality analysis to identify the most significant ESG factors. Using tools like Materiality Master can streamline this process, helping businesses align with the ESRS and provide stakeholders with actionable insights while complying with the CSRD.
5. Overcoming common challenges in reporting with the ESRS
While the ESRS offers many benefits, compliance can be challenging. Companies often struggle with:
- Data collection and validation, especially in companies with limited resources.
- Fast approaching deadlines for the implementation.
- Ensuring consistency across multiple reporting standards.
- Keeping up with the complexity of the ESRS and evolving requirements.
Large companies already have to comply with the CSRD in 2025, which means that the implementation has to be as easy and efficient as possible. Platforms like Materiality Master help companies to manage these complexities of CSR reporting. From conducting materiality assessments to organizing ESG data, these tools streamline the entire reporting process, ensuring compliance without overwhelming your team. Our Data Point Mapping Tool facilitates this process a lot as well, since it tells you exactly which ESRS Data Points have to be reported in your sustainability report.
Best practices for ensuring accurate data collection for reporting
Accurate data is the foundation of successful reporting. To ensure data integrity, companies should:
- Use standardized data collection methods.
- Engage cross-functional teams to gather relevant information.
- Regularly audit and review data for accuracy and completeness.
6. Leveraging the ESRS for competitive advantage
In a competitive marketplace, companies that lead in sustainability are often more attractive to investors, customers, and talent. By fully embracing the ESRS, your business demonstrates a commitment to sustainability that can differentiate you from competitors. The earlier businesses engage with EU regulations, the better prepared they will be for the coming years. Clear, transparent reporting through the ESRS can also help foster stronger relationships with key stakeholders. Investors will have more confidence in your risk management practices, customers will trust your sustainability efforts, and employees will be proud to work for a responsible company.
Compliance with the ESRS can also drive innovation. As companies work to meet these stringent reporting standards, they are often encouraged to find new ways to reduce environmental impacts, improve social outcomes, and enhance governance practices which helps the company in the short and long run, as well as society at large.
7. Conclusion: why you can’t afford to ignore the ESRS
As sustainability reporting becomes a core component of corporate governance, the ESRS stands out as the standard that will define business success in the coming years. Companies that fail to comply risk falling behind, while those that embrace the standards will unlock new opportunities for growth and innovation.
By understanding and implementing the ESRS today, you’ll future-proof your business for tomorrow’s challenges. Ready to get started? Tools like Materiality Master and the Datapoints Mapping tool can help streamline the process and ensure you meet every requirement.